College of Nursing
View Related Pages
Sunny Rana, RN, DNP, CRNA
 Sunny Rana, RN, DNP, CRNA
Sunny Rana, RN, DNP, CRNA
DNP Nurse Anesthesia
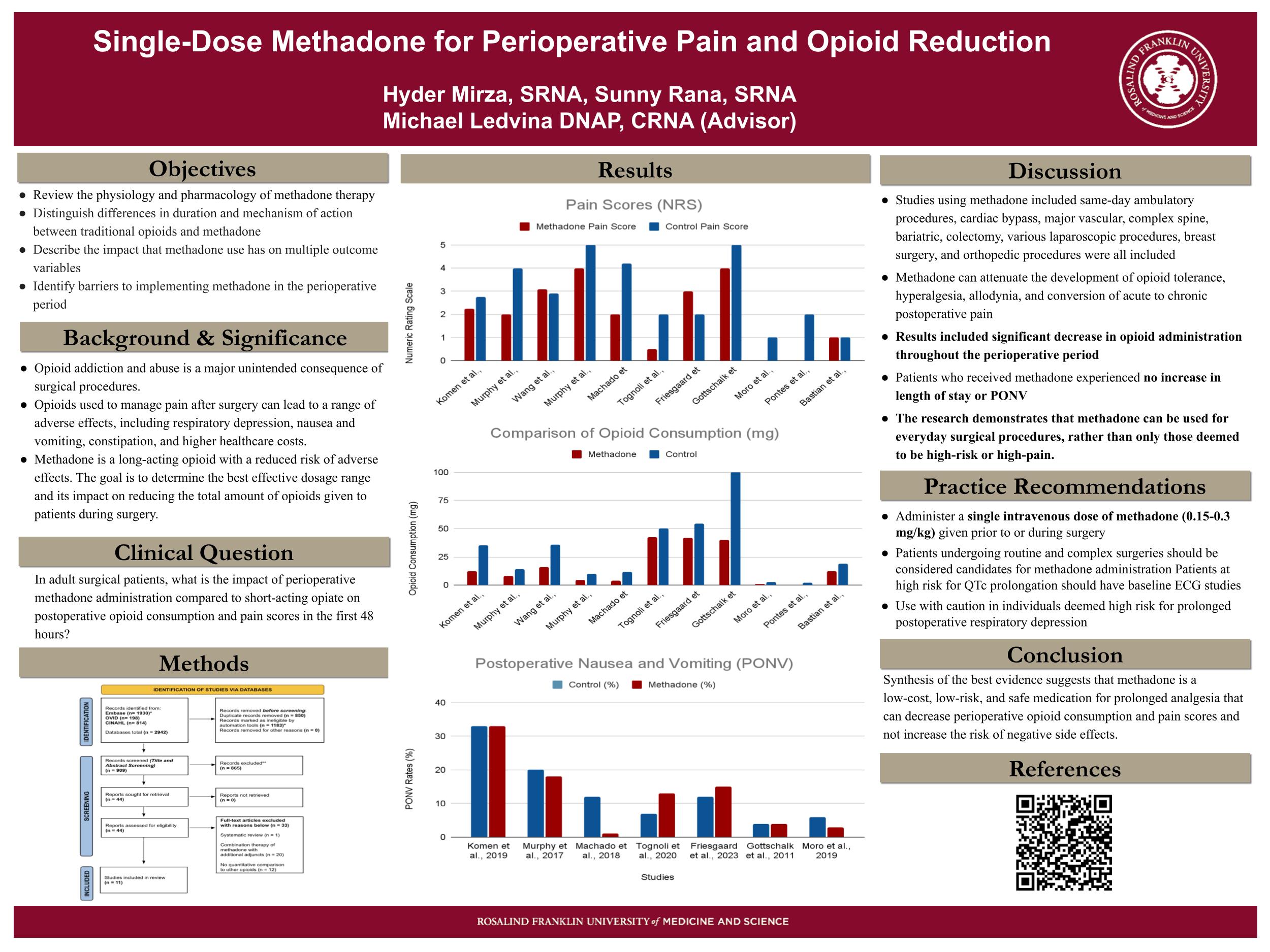
Single-Dose Methadone for Post-op Pain and Opioid Reduction
Project Category: Evidence Synthesis
Project Team: Sunny Rana, DNP, CRNA, Hyder Mirza, DNP, CRNA, Michael Ledvina, DNAP, CRNA (Advisor)
Abstract
Background: The potential for opioid addiction and abuse represents a significant unintended consequence of surgical procedures. The utilization of opioids for the management of postoperative pain can precipitate a range of adverse effects, including respiratory depression, nausea and vomiting, constipation, and an increased financial burden on healthcare systems. However, methadone, a long-acting opioid with a reduced incidence of adverse effects, is available to anesthesia providers. The objective is to ascertain the optimal effective dosage range and its impact on reducing the total amount of perioperative opioids administered to patients.
Methods: An integrative review was conducted by first utilizing a systematic search of PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and CINAHL. All randomized control trials (RCTs), and cohort studies that evaluated perioperative methadone administration to assess opioid use and pain relief were considered. The primary outcomes assessed were the number of morphine equivalents (MEq) administered perioperatively and level of pain postoperatively. Secondary outcomes included postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) and length of stay (LOS).
Results: A total of 872 subjects were compiled from eleven studies included in this review, 10 randomized controlled trials and one cohort study. Six out of the eleven studies reported a significant reduction in measured pain within the first 48 hours and seven studies showed significant reduction in opioid consumption and an insignificant effect on PONV and LOS.
Conclusion: The administration of 0.15-0.3 mg/kg of methadone in the perioperative setting has been demonstrated to significantly reduce the total amount of opioid use and to reduce post-operative pain levels. However, a reduction in PONV and LOS did not yield statistically significant results and therefore had no effect on PONV and LOS outcomes.